Compliance Management Best Practices –
Successfully Integrating Compliance In Your Organization
What you can expect
- Integration of compliance management into the Three Lines of Defence
- Anchoring of compliance management in existing structures of the organization
- Technical support for compliance management at strategic and operational levels

Author
Andreas Schleinzer is account manager and consultant specialized in integrated GRC, with an emphasis on data protection and compliance management.
Compliance management analyses and manages risks that can arise from non-compliance with regulatory requirements. These risks can take on different dimensions, from monetary effects to liability risks for management bodies. This definition shows how closely compliance management is tied to enterprise-wide risk management, as well as the internal control system. It’s therefore natural to include compliance management in the Three Lines of Defence. Analogous to the other management systems along the Second Line of Defence, compliance management can also be divided into the following three sub-areas:
- Governance
- Strategy
- Operational implementation within the departments
Governance
The governance activities for compliance management include scoping, as well as the definition of terms and the referral to normative references (e.g. to ONR 192050 or ISO 19600). This involves defining the scope of compliance management, which can be divided into two dimensions – defining the compliance topics, and defining the compliance-relevant processes. In addition to basic compliance with regulatory requirements and internal guidelines, the objectives of compliance management are also the reduction of liability risks for management.
Strategic Compliance Management
In accordance with the general definition of a governance function, strategic component of compliance management deals with planning in terms of processes and responsibilities, drawing up a list of standards, and supporting and advising the operational units. Specifically in the compliance area, activities at this level also include planning on how to deal with anonymous tips, or cases of damage that have occurred. Ensuring the effectiveness of the compliance management system (CMS) and internal and external communication round off the activities of strategic compliance management.
1 Planning by means of initial compliance risk assessment
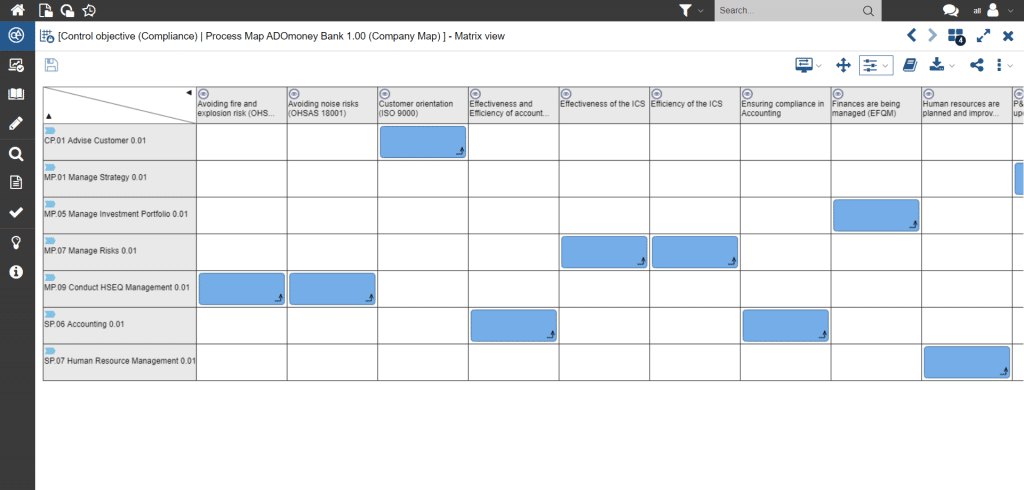
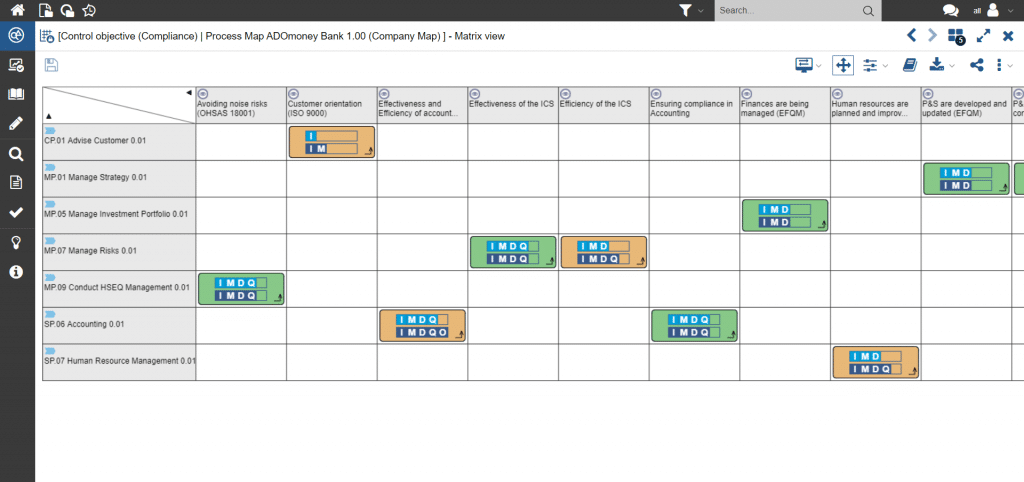
Based on the documented business processes, the prioritization of all compliance-relevant processes can be done using ADOGRC. There are assigned the standards which must be taken into account when carrying out the processes. As an example, this can be visualized as a matrix.
Figure 1: Allocation of compliance-relevant standards to corporate assets such as business processes or applications
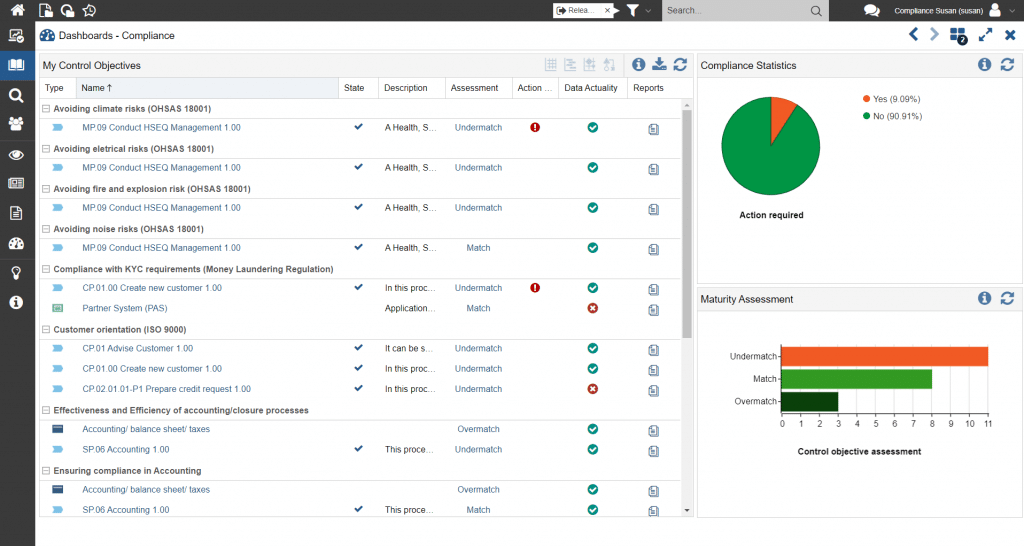
An overview of compliance can be accessed centrally in a dashboard, which can also be used on a topic-specific basis (e.g., on the topics of GDPR or money laundering prevention).
Figure 2: Compliance dashboard for enterprise-wide presentation of the fulfillment of compliance requirements
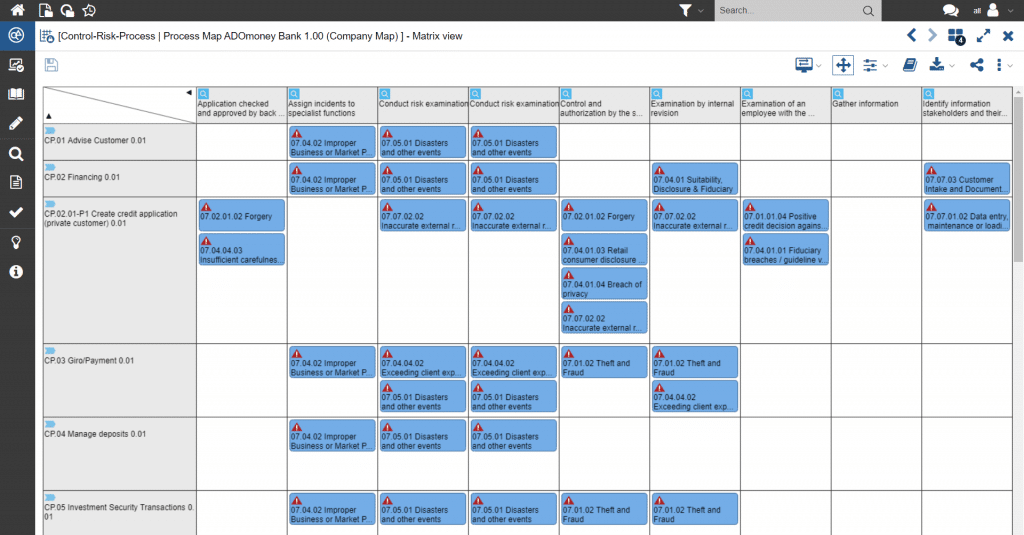
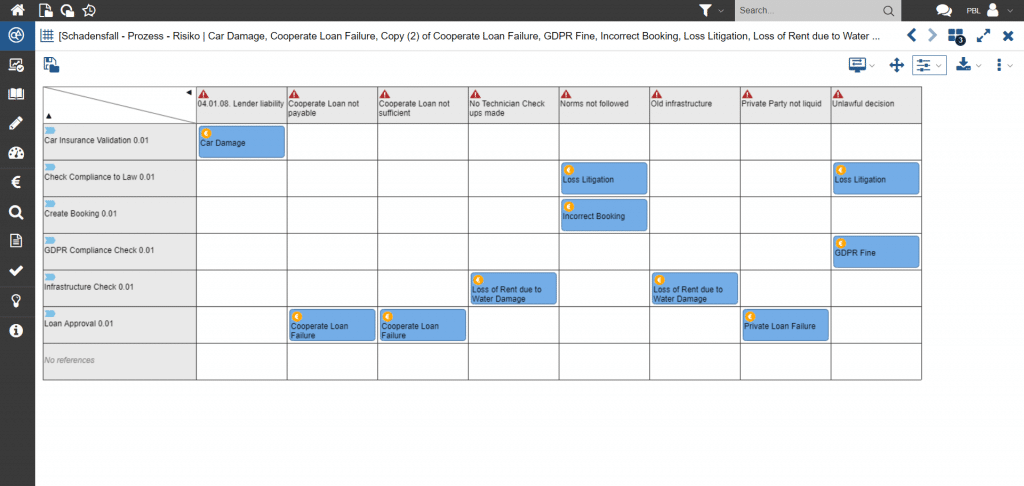
The possible compliance risks can be analysed based on the assessment regarding compliance. These can be managed with the help of the internal control system.
Figure 3: Compliance risk matrix with reference to all compliance-relevant processes and controls for managing risk
2 Monitoring implementation in the specialist areas
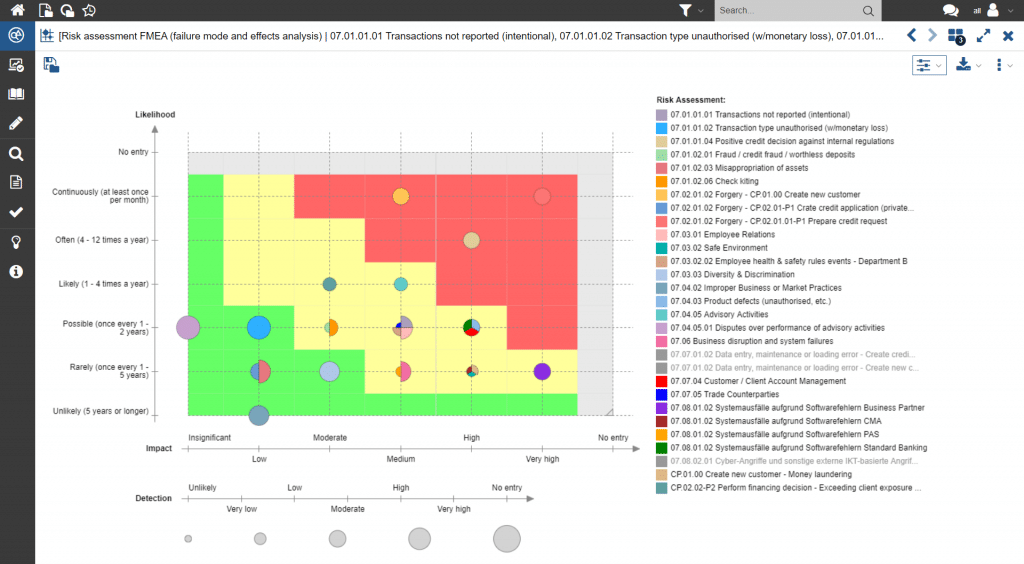
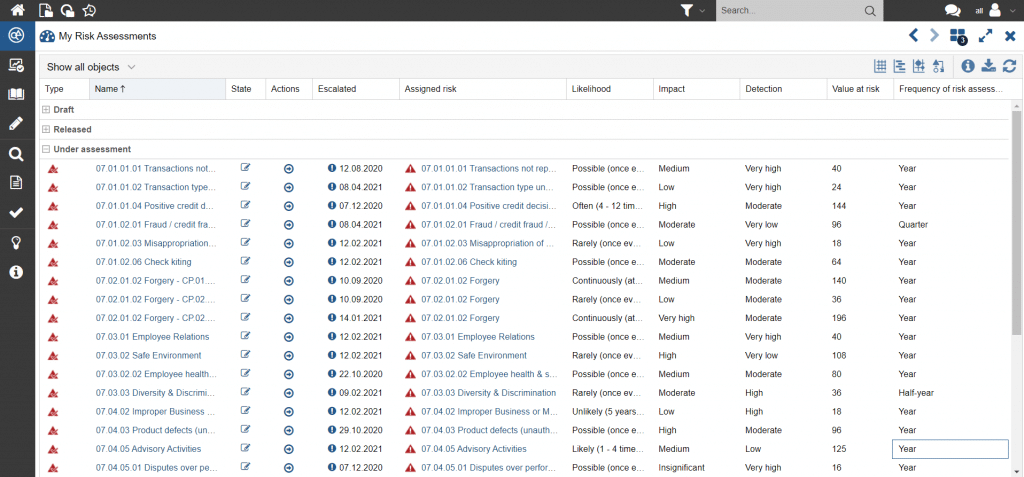
An initial risk analysis must be followed by regular updates of the risk portfolio, in line with the requirements of enterprise-wide risk management, so that the current risk situation in the compliance area can be called up at any time. This is facilitated by a workflow-supported risk assessment, which automatically notifies the second line of defence of problems in the individual assessments.
Figure 4: Compliance risk portfolio with reference to the probability and impact of the risk
Figure 5: Workflows and dashboard for efficient regular assessment and updating of compliance risks
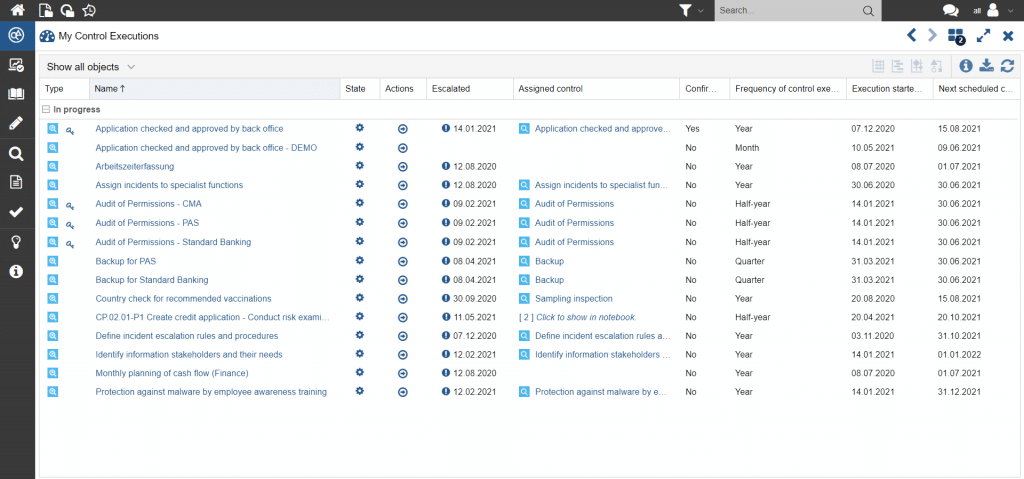
In addition to the ongoing risk assessment, monitoring also includes checking whether or not the recommended actions or controls have been carried out as planned to ensure that the risks have been managed. Here, workflow support facilitates the monitoring tasks as well.
Figure 6: Workflows and dashboard for efficient execution of compliance controls
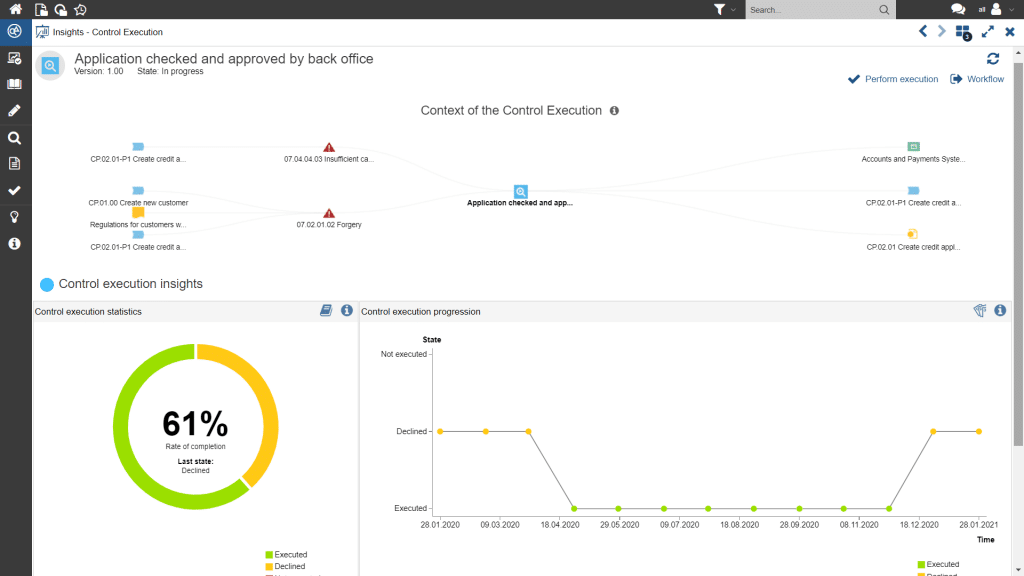
Figure 7: Overview of the quality of control implementation
Figure 8: Timing of compliance controls to ensure, among other things, that deadlines are met
3 Managing loss events
Despite all precautions, losses can occur and must be recorded and tracked transparently. Embedding losses in processes and risks provides valuable insights, which in turn lead to improvements in the processes themselves. Here, a workflow also ensures that losses are recorded and continuously updated in accordance with authorizations.
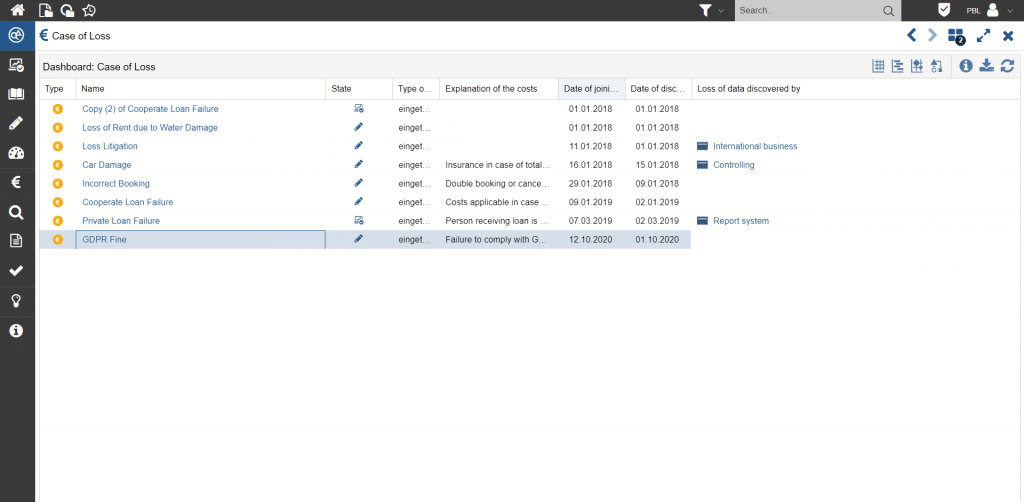
Figure 9: Dashboard with loss events in own area of responsibility or company-wide
Figure 10: Representation of damage events and their causative processes or associated risks
4 Evaluation and improvement through audits and measures
Compliance management, like other GRC functions, can use the possibilities of audits and measures to scale the progress of implementations, or make improvement suggestions using measures. The reference of audits to processes, organizational units and compliance topics, as well as the consideration of other aspects such as loss events, allow for transparent audit planning.
Figure 11: Audit planning taking into account audit-relevant topics with regards to the organizational units or processes
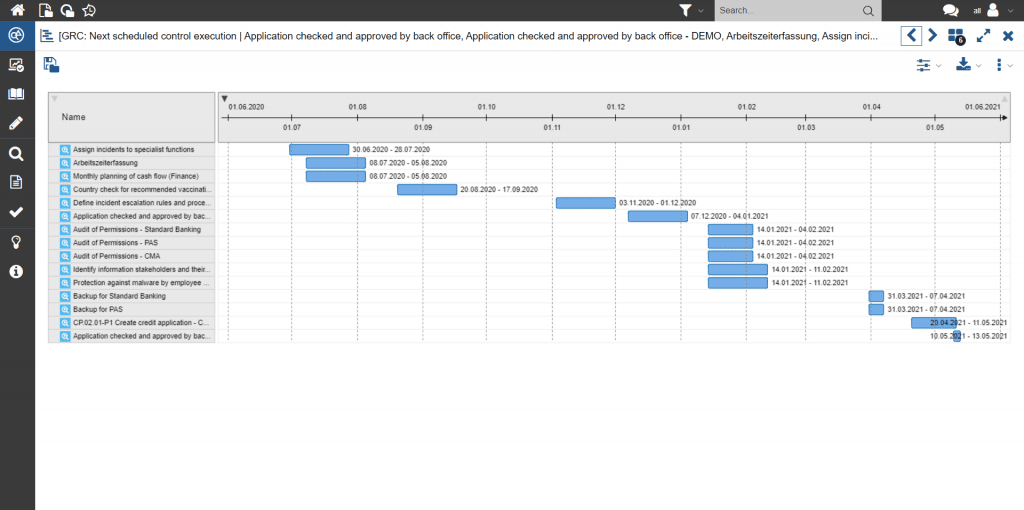
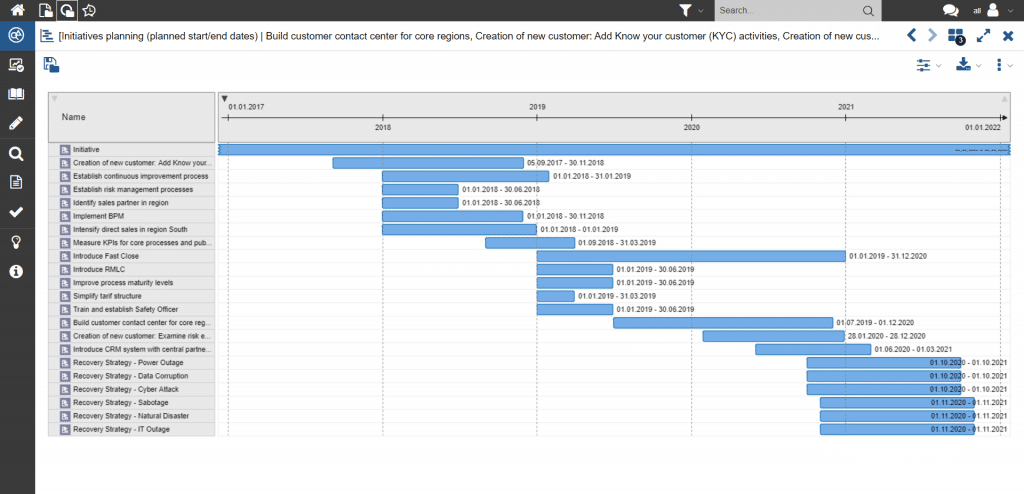
The implementation of taken measures can be tracked on a workflow basis. This provides the responsibles with an overview of the progress of the compliance measures at any time.
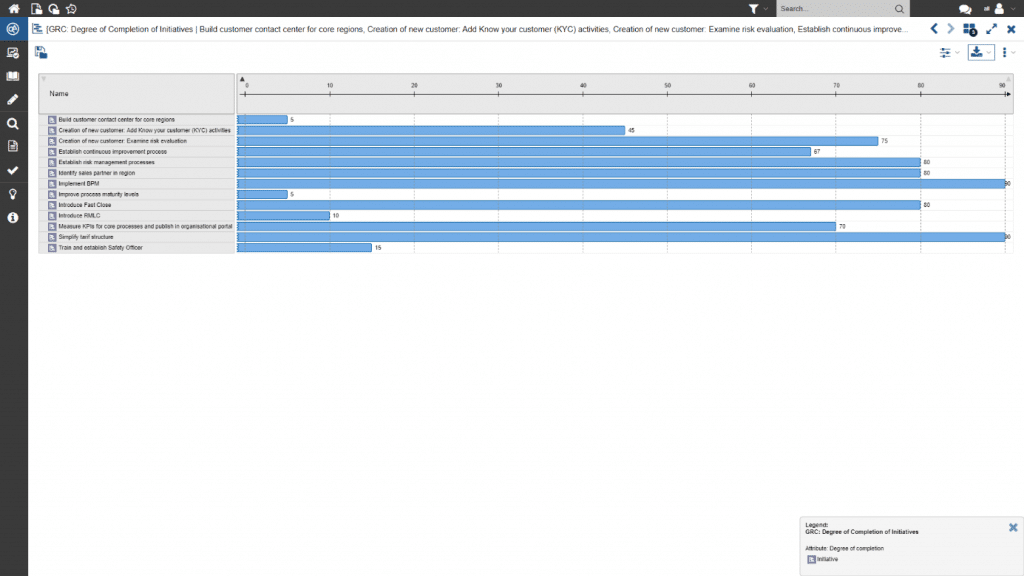
Figure 12: Representation of an action schedule using a Gantt view
Figure 13: Overview of compliance measures’ progress
Operational implementation within the departments
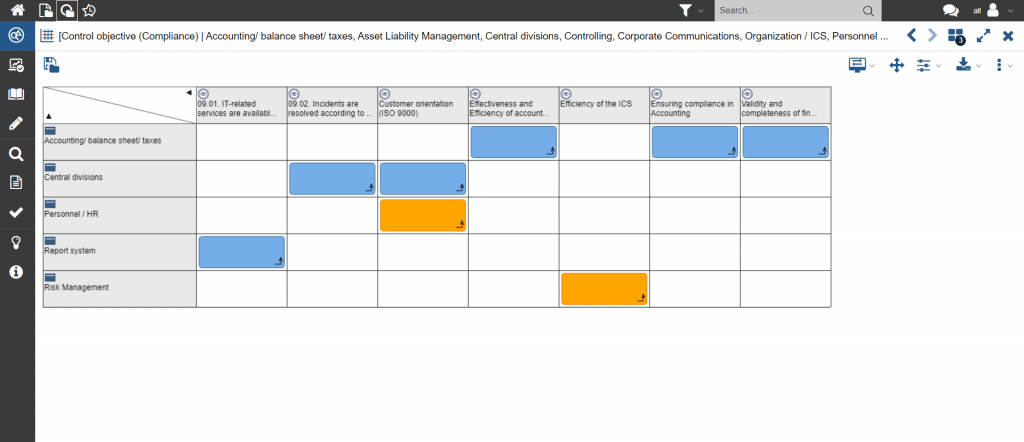
The operational implementation of compliance requirements is mostly carried out by taking into account the requirements in operational processes. The status regarding the fulfillment of the requirements in operational units can be showcased transparently with an assessment matrix.
Figure 14: Assessment of the degree of fulfillment of compliance requirements using an assessment matrix
In addition to the ongoing assessment of compliance, the tasks in the departments include:
- Regular assessment of compliance risks
- Implementation of controls to address compliance risk
- Recording and documentation of loss events
- Implementation of measures resulting from audits
Integrate your compliance management and increase your efficiency
By structuring your compliance management on the basis of the generic level model (governance / strategy / implementation), you can successfully integrate it with risk management and the internal control system in particular, based on the documentation of operational processes in the form of a process map. At the same time, the use of this process map enables efficient implementation of tasks in the departments responsible for ensuring compliance within the processes.
BOC Group has many years of experience in setting up an integrated compliance management in terms of the Three Lines of Defence. We offer expert advice, comprehensive tool support and training for successful implementation and continued operation. We would be happy to support you in successfully incoporating your compliance management in an integrated GRC system.